User Defined Function in SAP HANA:
User Defined Functions in SAP HANA are the read only
function that means we cannot perform any DDL and DML (insert update and
delete) operation inside the body of the function. There are two types of
user-defined functions: Scalar User Defined Functions and Table User Defined
Functions.
There
are two types of user define the function in SAP HANA:
1.
Table User Define Function (Table UDF)
2.
Scalar User Define Function (Scalar UDF)
These
categories are defined on the basis of input/output parameter, supported
functionality in the body of the function and how they are going to consume in
the SQL statement.
Scalar
Used-Defined Functions
The
simplest database object for which you can make use of SQL Script are Scalar
User- Defined Functions (Scalar UDFs)
Scalar
UDFs allow you to the define functions which take a number of input parameters
and return scalar values. Only expressions are allowed in the body of the UDF,
so no table operations, CE functions or array operations.
Scalar User-Defined Functions Support the Following:
·
They can have any number of scalar input
parameters (primitive SQL types). Input parameters of table type are not
supported.
·
They can return multiple scalar values.
·
They can contain expressions within their
body. Table and array operations are not supported.
·
They can be used in the field list or the
WHERE clause of SELECT statements — like built-in functions.
·
They are callable via direct assignment in
other user-defined functions or stored procedures
·
(x := my_scalar_func () ).
·
They must be free of side-effects and do
not support any type of SQL statement in their body.
The
SQL statement to define user-defined functions is create
function. The basic syntax to define a scalar user-defined function
looks as follows:
Basic Syntax to Define a Scalar User-Defined Function
CREATE
FUNCTION <function name> (<list of input parameters with
type>)
RETURNS
<scalar result parameter name and type>
AS
BEGIN
<function
body>
END;
v You
can create scalar user-defined functions for use like built-in functions.
v Prefix
parameter names with “:”to access their values.
Code:
To Create a table:
create
column table
"KABIL_PRACTICE"."OVERTIME"
(
"E_ID"
integer,
"E_NAME"
Nvarchar(35),
"OVERTIME(in_Hrs)"
Integer
);
To Drop a table:
Drop table
"KABIL_PRACTICE"."OVERTIME";
To Insert the values into a table:
Insert
into "KABIL_PRACTICE"."OVERTIME"
values (1,'Kabil',20);
Insert
into "KABIL_PRACTICE"."OVERTIME"
values (2,'Nazeer',15);
Insert
into "KABIL_PRACTICE"."OVERTIME"
values (3,'Kalai',10);
To Create function:
Create
Function "KABIL_PRACTICE"."CONVERT_HRS"
(i_Hours integer)
returns result Decimal(34,2)
as begin
result := :i_Hours * 60;
End;
NOTE:
We should not mention parameter name
inside the double quotes. If we did it throws an error such as inappropriate variable name: do not allow
"" or '_SYS_' prefix for the name of variable or parameter
To Call the function using Dummy:
select
"KABIL_PRACTICE"."CONVERT_HRS"(1)
from dummy;
Result:
To Use the function with the Table:
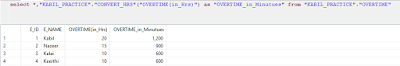
select
*,"KABIL_PRACTICE"."CONVERT_HRS"("OVERTIME(in_Hrs)")
as "OVERTIME_in_Minutues"
from "KABIL_PRACTICE"."OVERTIME";
Result:
To Drop a function:
Drop
function "KABIL_PRACTICE"."CONVERT_HRS";
NOTE:
The only way to change the body of an existing
user-defined function using SQL statements is to delete
the function and re-create it.
You can also use imperative logic in scalar
user-defined functions, to the extent this does not conflict with the
statements above. Imperative language constructs allow the developer to control
data and control flow, for example loops, scalar
variables and if-then-else statements.
Imperative Logic in SQLScript
Imperative
logic allows you to control the flow of the logic
·
Scalar variable
manipulation
·
Branching logic,
for example using if-then-else
·
Loops — while and
for
·
DDL statements and
insert, update and delete statements
Imperative
logic is executed exactly as scripted and procedural. It prevents parallel
processing.
Note:
DDL and DML are not supported in scalar user-defined
functions anyway. They can be used in table user-defined functions and database
procedures.
IF_THEN_ELSE Statements in Function Bodies:
CODE:
To Create Function IF_ELSE:
CREATE
FUNCTION "KABIL_PRACTICE"."Convert_Hours_IF_ELSE"(im_hours
INTEGER,im_to VARCHAR(1))
RETURNS
ex_result DEC (5,2)
AS BEGIN
IF :im_to = 'm'
THEN
ex_result := :im_hours * 60;
ELSEIF
:im_to = 'd' THEN
ex_result := :im_hours / 24;
ELSE
ex_result := :im_hours;
END IF;
END;
To Use the Function with the Table:
CODE 1:
SELECT
*, "KABIL_PRACTICE"."Convert_Hours_IF_ELSE"("OVERTIME(in_Hrs)",'m')
AS Overminutes FROM
"KABIL_PRACTICE"."OVERTIME";
Result:
CODE 2:
SELECT
*, "KABIL_PRACTICE"."Convert_Hours_IF_ELSE"("OVERTIME(in_Hrs)",'d')
AS Overminutes FROM
"KABIL_PRACTICE"."OVERTIME";
Result:
CODE 3:
SELECT
*, "KABIL_PRACTICE"."Convert_Hours_IF_ELSE"("OVERTIME(in_Hrs)",'')
AS Overminutes FROM
"KABIL_PRACTICE"."OVERTIME";
Result:
Thanks for visiting my Blog...
Share Your Comments...





good blog thank u so much
ReplyDeletegood blog with good content thank u so much oracle training in chennai
ReplyDeleteInfycle Technologies, the No.1 software training institute in Chennai offers the No.1 Selenium course in Chennai for tech professionals, freshers, and students at the best offers. In addition to the Selenium, other in-demand courses such as Python, Big Data, Oracle, Java, Python, Power BI, Digital Marketing, Cyber Security also will be trained with hands-on practical classes. After the completion of training, the trainees will be sent for placement interviews in the top companies. Call 7504633633 to get more info and a free demo.
ReplyDelete